The dental units are equipped with:
Compressed Air Supply: Dental units generally use compressed air. To do this, they are connected to an air compressor or to a central compressed air network. Compressors usually supply between 8 and 10 bars at the outlet of the tank, this pressure being too high for dental equipment. They can be obtained between 4.5 and 5.5 bars following the manufacturer’s recommendations, with a pressure reducer with a possible filter at the compressor outlet, for example. A good isolation of the consultation will be essential.
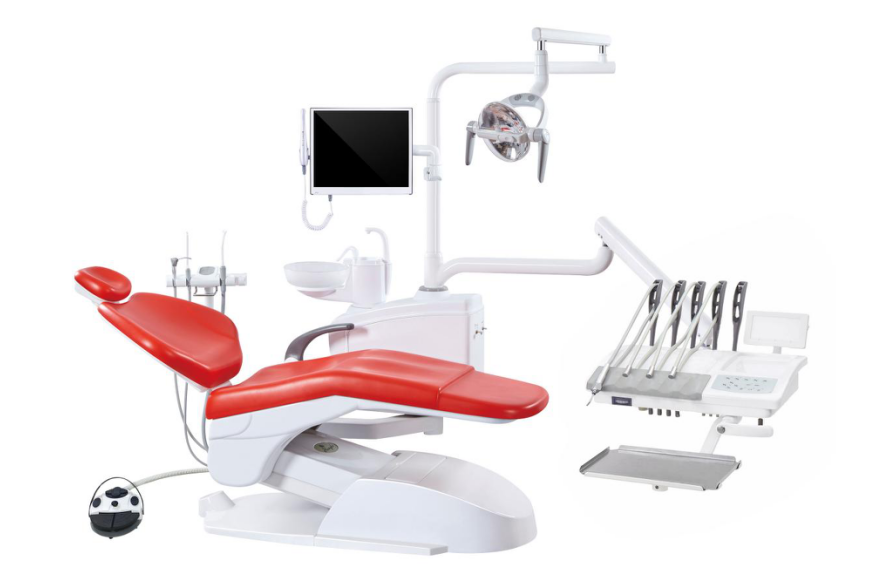
Water supply: the dental unitsThey must also be connected to a water supply for rinsing, cleaning and cooling functions. Water can cause many problems in dental units due to lime, sand, mud, rust or chlorine. Also, bacterial biofilms can quickly appear on the internal surfaces of connected pipes and reservoirs. To avoid such complications, the rule of thumb is that the clinic has an ergonomic, clean and efficient general stopcock and stops the supply every night. Old faucets that are difficult to access should be avoided. To control limescale in facilities, there are silicon phosphate cartridges that help combat deposits. Its shelf life is approximately six months.
Electrical supply: the components of the dental unit, as well as the instruments used during treatment, may require electrical power. This is the case of micromotors, among others.
Ergonomics: refers to the movement capacity of the station components, such as the chair or the instrument holder. Studies reveal that working with an instrument tray placed on the articulated arm, above the patient’s chest, is the best way to maintain a good balanced position without compromising the view of all tooth surfaces. It should also be noted that the dentist’s or assistant’s seat should be lower than that of the patient’s chair. In this position, the dentist’s spine retains its natural curvature, which avoids prolonged pressure on the intervertebral discs.
